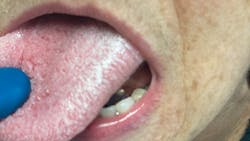
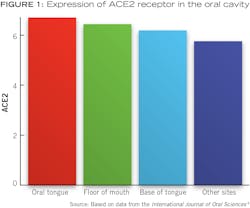
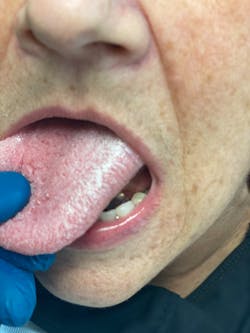
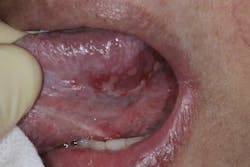
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)—an RNA virus that is the cause of novel coronavirus (COVID-19)—has known symptoms including fever, loss of smell and taste, headache, sore throat, dyspnea, dry cough, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.1 The effects of the virus on various organs are due to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, the portal of cellular entry for SARS-CoV-2, found in the lung, colon, heart, liver, kidney, gastrointestinal (GI) region, and nervous system.2
The proposed etiology of these lesions is thought to occur in two different ways and may be synergistic in fashion. The first suggested method is the result of viral binding to the oral epithelial cell’s ACE2 receptor and changes induced at the cellular level. The second proposed mechanism is allowing opportunistic infections brought about by other viruses, bacteria, and fungi in the oral cavity to cause disease due to COVID-19, stress, medications, and/or other related immunosuppressive factors compromising the immune system.
Treatment of these lesions attributed to “COVID tongue” is best rendered with proper diagnosis via a biopsy and/or DNA analysis from swab or saliva. In general, the literature has reported success treating these lesions with ointments or rinses consisting of neomycin, nystatin, and triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) applied three times a day.5 Compounded rinses containing nystatin, metronidazole, and essential oils have also been used in treatment. In addition, because COVID-19 can affect salivary quantity and quality, rinses addressing oral dryness and inflammation, such as StellaLife Vega oral rinse, can alleviate symptoms and expedite recovery. As with any disease affecting the tongue, a full complement of vitamins, including vitamin B3, vitamin B6, vitamin B9, vitamin B12, vitamin D, vitamin C, and zinc, should be considered.
Editor’s note: This article originally appeared in Perio-Implant Advisory, a chairside resource for dentists and hygienists that focuses on periodontal- and implant-related issues. Perio-Implant Advisory is part of the Dental Economics and DentistryIQ network. To read more articles, visit perioimplantadvisory.com and subscribe at this link.
Related reading:
- Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19
- Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus with over-the-counter products
- How does COVID-19 affect salivary flow and xerostomia?
- Loss of smell and taste: Distinguishing between COVID-19 and the common cold/flu
- Top 5 oral manifestations of COVID-19
References
- Symptoms of coronavirus. National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Division of Viral Diseases. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated December 22, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
- Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis MLC, Lely AT, Navis GJ, van Goor H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 2004;203(2):631-637. doi:10.1002/path.1570
- Xu H, Zhong L, Deng J, et al. High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):8. doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x
- Miller K. What is COVID tongue, and is it a sign you’ve been infected with the virus? Health. January 27, 2021. https://www.health.com/condition/infectious-diseases/coronavirus/covid-tongue-swollen
- Rodríguez MD, Romera AJ, Villarroel M. Oral manifestations associated with COVID-1. Oral Dis. 2020:10.1111/odi.13555. Published online: July 22, 2020. doi:10.1111/odi.13555
- Iranmanesh B, Khalili M, Amiri R, Zartab H, Aflatoonian M. Oral manifestations of COVID-19 disease: a review article. Dermatol Ther. 2020:e14578. Published online November 25, 2020. doi:10.1111/dth.14578
About the Author

Scott Froum, DDS
Editorial Director
Scott Froum, DDS, a graduate of the State University of New York, Stony Brook School of Dental Medicine, is a periodontist in private practice at 1110 2nd Avenue, Suite 305, New York City, New York. He is the editorial director of Perio-Implant Advisory and serves on the editorial advisory board of Dental Economics. Dr. Froum, a diplomate of both the American Academy of Periodontology and the American Academy of Osseointegration, is in the fellowship program at the American Academy of Anti-aging Medicine, and is a volunteer professor in the postgraduate periodontal program at SUNY Stony Brook School of Dental Medicine. He is a trained naturopath and is the scientific director of Meraki Integrative Functional Wellness Center. Contact him through his website at drscottfroum.com or (212) 751-8530.