Dental abscess caused by improper dental laser use
Technology is great … until it isn’t. Dental lasers have long been in use and have made advanced invasive procedures easier to perform with minimal healing required. Knowledge on how to use these lasers from both biological and clinical aspects is necessary to avoid adverse outcomes. This case study demonstrates what can happen when lasers are used incorrectly.
Case presentation
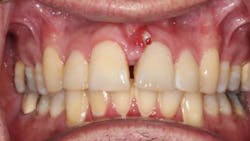
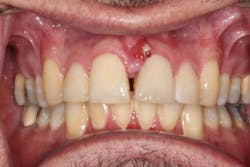
A 49-year-old male presented with pain at tooth no. 9. A labial fistula was clinically present (figure 1).
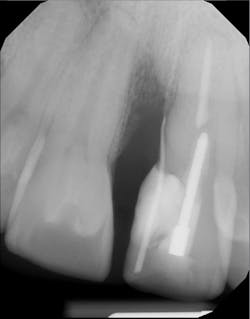
A periapical radiograph was taken to ascertain the source of the infection (figure 2).
Clinical examination
Examination revealed an area of necrotic bone (burnt dead bone), which was removed and submitted for histological evaluation. The pathology report came back as a maxillary anterior bone sequestrum or area of bone that has undergone necrosis (figure 3).
A review of the patient’s dental history revealed a very recent visit to a dentist for a laser surgical procedure. More than likely, improper use of the dental laser caused overheating of the bone and trauma to this area, ultimately resulting in bone necrosis and sequestra. Both hard- and soft-tissue loss resulted, and an abscess denoting infection occurred.
Because this is a maxillary anterior area in the esthetic zone, it will require interdisciplinary management and a high financial cost to the patient to correct the problem. Tooth rotation, the presence of a diastema, interproximal papilla, gingival margins and contours, as well as tooth size will all be addressed.
Conclusion
Advanced technology such as lasers are readily available to the dental profession, and although they can make treatment more efficacious and expeditious, there are inherent risks. Without adequate training, adverse complications can occur, making challenging situations even worse. The importance of training and proper biological rationale for use cannot be overstated.
Editor’s note: This article originally appeared in Perio-Implant Advisory, a chairside resource for dentists and hygienists that focuses on periodontal- and implant-related issues. Read more articles and subscribe to the newsletter.
About the Author
Tom Rubinstein, DMD
Tom Rubinstein, DMD, is a graduate of Rutgers University, where he majored in psychology with a focus in behavioral neuroscience. Dr. Rubinstein received his DMD from the University of Pennsylvania with honors in community service and clinical dentistry and was the recipient of multiple awards, including the Oral Health Foundation Dental Student Scholarship and Outstanding Dental Student in Implant Dentistry. After two years of General Practice Residency at NYU Langone Brooklyn, he completed his periodontal specialty training at Columbia University, where he served as chief resident and received the Murray Schwartz Scholarship and Lionel Abzug Award. He is a member of the American Academy of Periodontology and the American Dental Association.
Updated November 8, 2022
Markus L. Weitz, DDS
Markus L. Weitz, DDS, began private practice in 1988 and has been on the forefront of dental implantology since its introduction into dentistry. He was among the first in the community to place dental implants and has led the development of protocols for immediate implant placement and restoration. As a result, his patients usually leave the office with fixed (nonremovable) teeth the day they receive implants and can expeditiously complete treatment. Dr. Weitz is certified in the use of a special laser protocol, LANAP, for the noninvasive and nonsurgical treatment of gum disease as an alternative to traditional surgery.
Updated November 8, 2022