Oral manifestations in COVID-19–positive patients: 8 case reports
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) presents with flulike symptoms—fever, cough, loss of smell and taste, and body aches, to name a few.1,2 In immunocompromised patients, COVID-19 can lead to lethal respiratory distress.3 SARS-CoV-2 binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is detected in the cell membrane of numerous human organs and tissues, including the lungs, kidneys, liver, epithelial cells of the tongue and salivary glands, upper respiratory tract, nervous system, and skeletal muscle, among others.4
Many studies suggest that the cells expressing ACE2 enzymes are considered to be host cells for the COVID-19 virus. The ACE2 enzyme is highly expressed in type II alveolar cells of the lungs as well as on the epithelial cells of the tongue.5 The saliva is a medium for transmission of various microorganisms, including herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and MRSA bacteria. Oral manifestations seen in patients with COVID-19 can be due to virus itself and/or the decreased immunity in these individuals. Many studies have reported that the rashlike lesion that occurs is due to proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 in the oral cavity, which is caused by decreased immunity. The epithelial cells on the tongue are rich in ACE2 enzymes, which aid in the multiplication of SARS-CoV-2.
The oral lesions observed in COVID-19–positive patients may be due to the virus breeding in saliva, decreased immunity, or a reaction to antiviral medications.6 There have been reports that oral manifestations precede typical respiratory symptoms seen with COVID-19. Symptoms such as anosmia (lack of smell) and dysgeusia (lack of taste) were also reported in many COVID-19 studies.7 These manifestations suggest that SARS-CoV-2 virus might have the ability to target the oral mucous membrane.
This article describes eight different cases of oral manifestations seen in patients testing positive for COVID-19. Moreover, the article highlights the management of such cases.
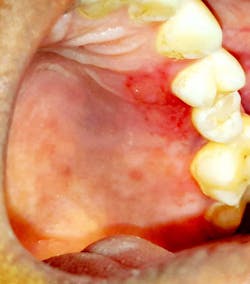
Case no. 1
The provisional diagnosis was COVID-19–related oral lesions. The case was managed using topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste, doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinse, and topical lignocaine 2% gel three times per day.
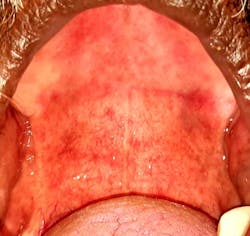
Case no. 2
The provisional diagnosis was COVID-19–related oral lesions. The case was managed with topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste, doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinses, and topical benzocaine 5% gel.
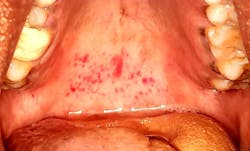
Case no. 3
The provisional diagnosis was COVID-19–related oral lesions. Topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste, doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinses, and topical benzocaine 5% gel were prescribed three times per day.
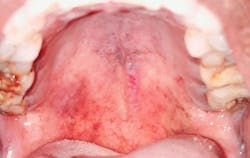
Case no. 4
The tentative diagnosis noted was COVID-19–related oral lesions. The lesions were addressed with topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste, doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinses, and topical benzocaine 5% gel, thrice daily.
Case no. 5
The provisional diagnosis was COVID-19–related oral lesions. The case was managed with topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste, and doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinses.
Case no. 6
The tentative diagnosis was COVID-19–related oral lesions. The lesions were addressed with topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste, doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinses, and topical lidocaine 2% gel three times per day.
Case no. 7
The case was managed with doxycycline mouthrinses, topical benzocaine gel 5%, and polyvitamin supplements thrice daily for 14 days.
Case no. 8
The case was managed with doxycycline mouthrinses, topical benzocaine gel 5%, and polyvitamin supplements thrice daily for 14 days.
Summary
Conclusion
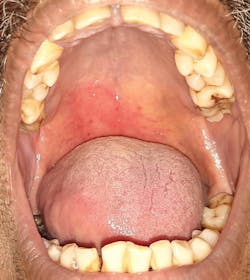
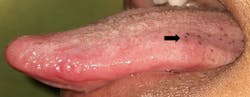
The COVID-19–positive patient presents with a variety of oral lesions, which include:
- Multiple palatal and oropharyngeal petechial lesions
- Dysgeusia
- Palatal and oropharyngeal erosions and ulcerative lesions
- Excessive salivation
- Severe pain over the lesion area
- Partial paresthesia surrounding the lesions
- Irregular areas of blanching involving the palate
- Burning sensation of palate and oropharynx, and dysphagia
- Palatal and oropharyngeal tenderness and soreness
- Necrotic pseudomembranes covering the erosive/ulcerative lesions
Management protocol A management protocol for COVID-19–positive patients is as follows:
- Topical triamcinolone acetonide (Kenacort) 0.1% paste (applied by the patient three times daily)
- Doxycycline and benzalkonium chloride mouthrinses (applied by the patient three times daily)
- Topical benzocaine 5% gel (applied by the patient three times daily)
All photos courtesy of the author
Editor’s note: This article originally appeared in Perio-Implant Advisory, a chairside resource for dentists and hygienists that focuses on periodontal- and implant-related issues. Perio-Implant Advisory is part of the Dental Economics and DentistryIQ network. To read more articles, visit perioimplantadvisory.com and subscribe at this link.
References
- Singhal T. A review of coronavirus disease–2019 (COVID-19). Indian J Pediatr. 2020;87(4):281-286. doi:10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6
- Lo Giudice R. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus–2 (SARS CoV-2) in dentistry. Management of biological risk in dental practice. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(9):3067. doi:10.3390/ijerph17093067
- Yi Y, Lagniton PNP, Ye S, Li E, Xu RH. COVID-19: what has been learned and to be learned about the novel coronavirus disease. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(10):1753-1766. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45134
- Salamanna F, Maglio M, Landini MP, Fini M. Body localization of ACE-2: on the trail of the keyhole of SARS-CoV-2. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:594495. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.594495
- Fini MB. Oral saliva and COVID-19. Oral Oncol. 2020;108:104821. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104821
- Xu H, Zhong L, Deng, J, et al. High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):8. doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x
- Carrillo-Larco RM, Altez-Fernandez C. Anosmia and dysgeusia in COVID-19: a systematic review. Wellcome Open Res. 2020;5:94. doi:10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15917.1
- Rodríguez MD, Romera AJ, Villarroel M. Oral manifestations associated with COVID-19. Oral Dis. 2020;10.1111/odi.13555. doi:10.1111/odi.13555
- Wadia R. COVID-19 – oral manifestations. Br Dent J. 2020;229(10):669. doi:10.1038/s41415-020-2411-z
- Hamishehkar H, Nokhodchi A, Ghanbarzadeh S, Kouhsoltani M. Triamcinolone acetonide oromucoadhesive paste for treatment of aphthous stomatitis. Adv Pharm Bull. 2015;5(2):277-282. doi:10.15171/apb.2015.038
- Lewis MAO, Wilson NHF. Oral ulceration: causes and management. The Pharmaceutical Journal. March 19, 2019. https://www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/cpd-and-learning/learning-article/oral-ulceration-causes-and-management/20205786.article
- Altenburg A, El-Haj N, Micheli C, Puttkammer M, Abdel-Naser MB, Zouboulis CC. The treatment of chronic recurrent oral aphthous ulcers. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014;111(40):665-673. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2014.0665
Dr. Aravindhan Karunakaran is an associate professor and head of the department of oral medicine and radiology at Konaseema Institute of Medical Sciences Dental College in India.
About the Author
Dr. Aravindhan Karunakaran
Dr. Aravindhan Karunakaran is an associate professor and head of the department of oral medicine and radiology at Konaseema Institute of Medical Sciences Dental College in India.